RMI Tutorial for Java Beginners
11:45:00
For easy understanding of RMI concept, RMI Tutorial is given in
Questions and Answers format. Remote method
invocation(RMI) allow a java object to invoke method on an object running on
another machine. RMI provide remote communication between java program. RMI is
used for building distributed application.
Concept of RMI application
A RMI application can
be divided into two part,Client program and Server program. A Server program creates some remote object, make their
references available for the client to invoke method on it. A Client program make request for remote objects on
server and invoke method on them. Stub and Skeleton are two important object used for
communication with remote object.
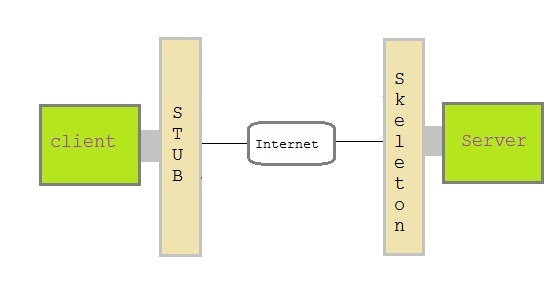
Stub and Skeleton
Stub act as
a gateway for Client program. It resides on Client side and communicate with Skeleton object. It establish the connection between
remote object and transmit request to it.
Skeleton object resides
on server program. It is responsible for passing request from Stub to remote object.
Creating a Simple RMI
application involves following steps
·
Define a remote
interface.
·
Implementing remote
interface.
·
create and start remote
application
·
create and start client
application
1.
What is Java RMI?
RMI stands for
"Remote Method Invocation", the technology of Java.
2.
What is remote method?
A method of a
Java program placed on any other system (not in your own system) in the world.
3.
Then what is invocation?
Sending a
request to the other system (say, a server) to execute the method (say, to call
as remote method) available on it by passing sufficient parameters required for
the execution of the method and asking to return the return value of the
method.
Finally, RMI is
nothing but communication between two JVMs loaded on two different systems.
4.
Give a practical example, to be more clear in this RMI tutorial?
Take an example
of a Bank ATM operation. Suppose you are to ATM to
know the account balance. You know the balance is available on the bank server
and not on ATM machine (say, ATM client). When you swipe your card your account
number goes into the machine and inform the machine that you need to know the
balance by clicking the button. Now there are two values to be send to the
server (we call these as parameters later), one is account number and the other
is what the operation you need.
Now imagine,
there is a method on the server (we call remote method as it is not avilable on
your local ATM system) which will take care of your need, say "public double getBalance(int
accountNumber, double retrieveBalance)". Now RMI job is to
take your information and send it as parameters to the remote method, execute
the method and send back the account balance as return value to the ATM client
to print the label.
This is exactly
what RMI application does.
5.
What is distributed communication? Explain for beginners
RMI sort of
communication is an example of distributed communication where systems are
distributed across the globe. Here Internet is not used and where it differs
with Servletcommunication. The systems involved in
communication are known as distributed systemsand programming is known as distributed computing. If required, RMI can be connected to Internet to communicate
with Web servers.
6.
What a distributed application should satisfy?
A distributed
application needs the following to do.
1.
The client should be able to locate the remote objects existing
on remote server. For example, RMI uses a naming service given by Naming class
to bind remote objects with the rmi registry.
2.
The client should be able to communicate with the remote
objects. This is taken care by RMI runtime environment.
RMI programming feels in such way the remote method invocation is as if
invoking on a local system. Small difference comes in Server side program where
binding is performed by the remote object with the RMI runtime mechanism
through RMI registry.
3.
To load methods for objects used in invocation. RMI passes
objects between client and server and loads methods as per need.
7.
As it given an example of bank transaction, does RMI take care of transaction
management also?
No, RMI job is
communication only – sending parameters to the remote method and getting back
the return value of the remote method to the client. To take care of
transactions, takes the help of EJB (Enterprise Java Beans). The backbone of
EJB is RMI. EJB uses RMI for communication and adds extra features like
transaction management, security, atomicity, load balancing and logging etc.
8.
What protocol RMI uses?
First of all you
know it is not a Web based technology. So, RMI does not use browsers and HTTP
protocol. It comes with its own protocol known as RMI protocol with a default port number 1099 (which you can configure of your own). The protocol involves RMI
runtime environment, Remote references for remote objects, RMI registry and
some naming service etc.
9.
What is object communication?
In RMI, objects
communicate; an object on client side communicates with another object on
server side. This is known as object-to-object communication. Through distributed network, objects
pass in between client and server (having reference to each other). For this
purpose, RMI internally serialize objects. This is good example where Java uses objects most
extensively in programming.
10. What is remote object?
An object
created on the server (by the server program) is known as remote object. To put technically, any object that implements java.rmi.Remote interface is known as remote object. This we is shown how to
create in RMI Application Step by Step Programs Explanation (in 3rd Program – server program).
11.
What are the features of RMI?
1.
It is object-oriented and communication is between Java-to-Java
objects distributed.
2.
It is multithreaded.
3.
All the features of Java are applicable to RMI.
4.
The extended Java features are: a) Distributed connectivity b)
Connecting legacy systems. Legacy means that we do not know in advance what
type of server it is going to be connected in the network.
5.
RMI is seamless integration.
Seamless implies communication through an object and information about
operating system where the object developed is not known to the programmer when
he writes the code.
6.
RMI has different type of garbage collection known as Distributed garbage collection.
12.
What is distributed garbage collection?
Everyone knows what is
garbage collection in Java – removing objects that do not have any reference
(not used) in the remaining part of the Java program being executed. All this
happens on a single system. But distributed garbage collection is very
different as it occurs between two systems. In RMI, the server exports a object
to the client by storing a reference with it. When the client communication is
over or disconnects with the server, the reference of client is lost on the
server remote object. If the reference of the client no more exists, the remote
object on the server is eligible for garbage collection. This is known as distributed garbage collection. Remote objecct and the reference are
explained in RMI Application Step by Step Programs Explanation (in 4th Program – client program).
13.
What is the architecture of RMI?
RMI as a
technology comes with an architecture, implementation with distribution of
client and server side programs and execution etc. Architecture is given in Java RMI Architecturewith
diagram.
14.
How many layers exists in RMI Architecture?
Basically there
are three layers – Application layer, Proxy layer and Remote reference layer. These are discussed in RMI architecture clearly.
15. What an RMI application comprises of?
The basic
programs needed for an RMI application are a remote interface, stub and
registry etc. All these are discussed in
RMI Application Step by Step Programs Explanation and execution.
RMI Application Step by Step Programs Explanation and execution.
16. What is the process of compilation, execution and
distribution (on client and server) of the programs involved in RMI
application?
Compilation and
execution are clearly given step-by-step in RMI Stepwise Compilation Execution Distribution.




0 comments
Thanks for intrest.. We will touch withbyou soon..