Java Access Modifiers
14:42:00Access Modifiers in java
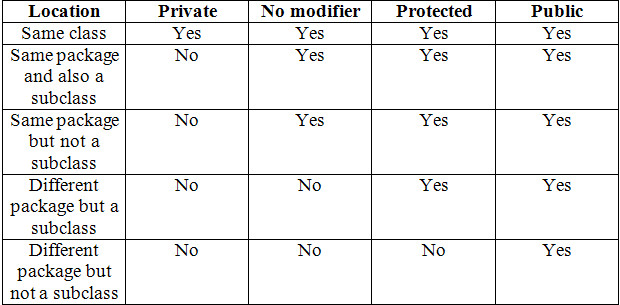
There are two types of access modifiers
in java: access modifiers and non-access modifiers.
The access modifiers in java specify
accessibility (scope) of a data member, method, constructor or class.
There are 4 types of java access
modifiers:
- private
- default
- protected
- public
There are many non-access modifiers
such as static, abstract, synchronized, native, volatile, transient etc. Here,
we will learn access modifiers.
1) private access modifier
|
The private access modifier is
accessible only within class.
|
Example of private access modifier
|
In this example, we have created
two classes Demo and Test. Demo class contains private data member and
private method. We are accessing these private members from outside the
class, so there is compile time error.
|
|
1.
class Demo{
2.
private int data=40;
3.
private void msg1(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
4.
}
5.
6.
public class Test{
7.
public static void main(String args[]){
8.
Demo obj=new Demo();
9.
System.out.println(obj.data);//Compile Time Error
10.
obj.msg1();//Compile Time Error
11.
}
12.
}
|
2) default access modifier
|
If you don't use any modifier,
it is treated as default bydefault.
The default modifier is accessible only within package.
|
Example of default access modifier
|
In this example, we have created
two packages pack and mypack. We are accessing the A class from outside its
package, since A class is not public, so it cannot be accessed from outside
the package.
|
In the above example, the scope of class A and
its method msg() is default so it cannot be accessed from outside the package.
3)
protected access modifier
The protected access modifier is accessible within package and outside the
package but through inheritance only.
The protected access modifier can be applied on the data member, method
and constructor. It can't be applied on the class.
Example of protected access modifier
In this example, we have created the two packages pack and mypack. The A
class of pack package is public, so can be accessed from outside the package.
But msg method of this package is declared as protected, so it can be accessed
from outside the class only through inheritance.
|
1.
/save by A.java
2.
package pack;
3.
public class A{
4.
protected void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
5.
}
|
|
1.
//save by B.java
2.
package mypack;
3.
import pack.*;
4.
5.
class B extends A{
6.
public static void main(String args[]){
7.
B obj = new B();
8.
obj.msg();
9.
}
10.
}
|
4) public access modifier
|
The public
access modifier is
accessible everywhere. It has the widest scope among all other modifiers.
|
Example of public access modifier
|
1.
//save by A.java
2.
3.
package pack;
4.
public class A{
5.
public void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
6.
}
|
|
1.
//save by B.java
2.
3.
package mypack;
4.
import pack.*;
5.
6.
class B{
7.
public static void main(String args[]){
8.
A obj = new A();
9.
obj.msg();
10.
}
11.
}
|






0 comments