Polymorphism in Java
18:31:00
Polymorphism
in Java
Polymorphism
is the capability of a method to do different things based on the object that
it is acting upon. In other words, polymorphism allows you define one interface
and have multiple implementations. I know it sounds confusing. Don’t worry we
will discuss this in detail.
Polymorphism
is derived from 2 greek words: poly and morphs. The word "poly" means
many and "morphs" means forms. So polymorphism means many forms.
Real
life example of polymorphism..!
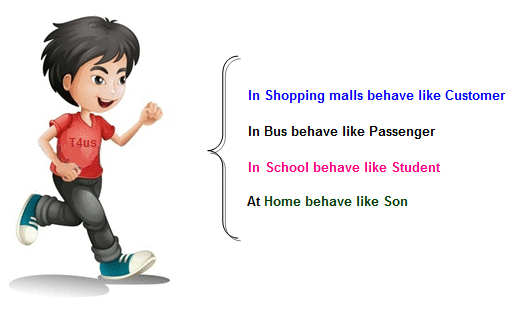
Suppose
if you are in class room that time you behave like a student, when you are in
market at that time you behave like a customer, when you at your home at that
time you behave like a son or daughter, Here one person present in
different-different behaviors.
It is a
feature that allows one interface to be used for a general class of actions.
- An operation may exhibit different behavior in different instances.
- The behavior depends on the types of data used in the operation.
- It plays an important role in allowing objects having different internal structures to share the same external interface.
- Polymorphism is extensively used in implementing inheritance.
- Following concepts demonstrate different types of polymorphism in java.
How to
achieve Polymorphism in Java ?
In java
programming the Polymorphism principal is implemented with method overriding
concept of java.
Polymorphism
principal is divided into two sub principal they are:
1)
Method Overloading or Compile Time
Polymorphism
2)
Method Overriding or Run Time Polymorphism
What is
a Method Definition:
A method
is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at
any point in a program simply by utilizing the method’s name.
I. Method
Overloading
If with in a one class more than one same Method name exit in the sense
its called Method overloading or compil time polymorphism.
Example of Method Overloading :
By
changing the no. of arguments
In
this example, we have created two overloaded methods, first sum method performs
addition of two numbers and second sum method performs addition of three
numbers.
1.
class Calculation{
2.
void sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
3.
void sum(int a,int b,int c){System.out.println(a+b+c);}
4.
5.
public static void main(String args[]){
6.
Calculation obj=new Calculation();
7.
obj.sum(10,10,10);
8.
obj.sum(20,20);
9.
10.
}
11.
}
|
Output:30
40
|
Example of Method Overloading:
By
changing data type of argument
In
this example, we have created two overloaded methods that differs in data type.
The first sum method receives two integer arguments and second sum method
receives two double arguments
.
1.
class Calculation2{
2.
void sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
3.
void sum(double a,double b){System.out.println(a+b);}
4.
5.
public static void main(String args[]){
6.
Calculation2 obj=new Calculation2();
7.
obj.sum(10.5,10.5);
8.
obj.sum(20,20);
9.
10.
}
11.
}
|
Output:21.0
40
|
Why Method Overloaing is not
possible by changing the return type of method?
In
java, method overloading is not possible by changing the return type of the
method because there may occur ambiguity. Let's see how ambiguity may occur:
because
there was problem:
1.
class Calculation3{
2.
int sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
3.
double sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
4.
5.
public static void main(String args[]){
6.
Calculation3 obj=new Calculation3();
7.
int result=obj.sum(20,20); //Compile Time Error
8.
9.
}
10.
}
|
Result : int result=obj.sum(20,20); //Here how can java determine
which sum() method should be called
|
Can we overload main() method?
Yes,
by method overloading. You can have any number of main methods in a class by
method overloading. Let's see the simple example:
1.
class Overloading1{
2.
public static void main(int a){
3.
System.out.println(a);
4.
}
5.
6.
public static void main(String args[]){
7.
System.out.println("main() method invoked");
8.
main(10);
9.
}
10.
}
|
Output:main() method invoked
10
|
Advantage of method overloading?
Method
overloading increases the readability of the
program.
Different ways to overload the
method
There are two ways to overload the
method in java
|
- By
changing number of arguments
- By
changing the data type
Rules for Method
Overloading
1. Overloading can take place in the same class
or in its sub-class.
2. Constructor in Java can be overloaded
3. Overloaded methods must have a different
argument list.
4. Overloaded method should
always be the part of the same class(can also take place in sub
class), with same name but different parameters.
5. The parameters may differ in their type or
number, or in both.
6. They may have the same or different return
types.
7. It is also known as compile time polymorphism.
II.Method Overriding
Child class has the
same method as of base class. In such cases child class overrides the parent
class method without even touching the source code of the base class. This
feature is known as method overriding.
Example:
Example:
Runtime polymorphism or Dynamic
Method Dispatch is a process
in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than
compile-time.
In this process, an overridden method is called through the
reference variable of a superclass. The determination of the method to be
called is based on the object being referred to by the reference variable.
Upcasting
When reference variable
of Parent class refers to the object of Child class, it is known as upcasting.
1. class A{}
2. class B extends A{}
|
A a=new B();//upcasting
|
Real example of Java
Runtime Polymorphism
Consider a scenario,
Bank is a class that provides method to get the rate of interest. But, rate of
interest may differ according to banks. For example, SBI, ICICI and AXIS banks
could provide 8%, 7% and 9% rate of interest.
1. class Bank{
2. int getRateOfInterest(){return 0;}
3. }
4.
5. class SBI extends Bank{
6. int getRateOfInterest(){return 8;}
7. }
8.
9. class ICICI extends Bank{
10.
int getRateOfInterest(){return 7;}
11.
}
12.
class AXIS extends Bank{
13.
int getRateOfInterest(){return 9;}
14.
}
15.
16.
class Test3{
17.
public static void main(String args[]){
18.
Bank b1=new SBI();
19.
Bank b2=new ICICI();
20.
Bank b3=new AXIS();
21.
System.out.println("SBI Rate of Interest: "+b1.getRateOfInterest());
22.
System.out.println("ICICI Rate of Interest: "+b2.getRateOfInterest());
23.
System.out.println("AXIS Rate of Interest: "+b3.getRateOfInterest());
24.
}
25.
}
|
Output:
SBI Rate of Interest: 8
ICICI Rate of Interest: 7
AXIS Rate of Interest: 9
|
Rules for
Method Overriding:
1. applies
only to inherited methods
2. object
type (NOT reference variable type) determines which overridden method will be
used at runtime
3. Overriding
method can have different return type (refer this)
4. Overriding
method must not have more restrictive access modifier
5. Abstract
methods must be overridden
6. Static
and final methods cannot be overridden
7. Constructors
cannot be overridden
8. It
is also known as Runtime polymorphism.
super keyword in
Overriding:
When invoking a
superclass version of an overridden method the super keyword is used.
Example:
Example:
class Vehicle {
public void move () {
System.out.println ("Vehicles are used for moving from one place to another ");
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
public void move () {
super. move (); // invokes the super class method
System.out.println ("Car is a good medium of transport ");
}
}
public class TestCar {
public static void main (String args []){
Vehicle b = new Car (); // Vehicle reference but Car object
b.move (); //Calls the method in Car class
}
}
|
Output:
Vehicles are used for moving from one place to another
Car is a good medium of transport
|
Difference Between Method Overloading vs Method Overriding







0 comments